Add AWS/Azure/Google Cloud Data Store
This section provides information about how to add AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud data store as a destination.
Note: Creating the AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud data store is not supported on a GUID or on a volume mounted without a drive letter.
Follow these steps:
- On the Protect screen, do one of the following:
- Navigate to Destinations > Recovery Point Servers.
- From the list of recovery point servers, click the Action drop-down list of a specific recovery point server, and then select Add AWS/Azure/Google Cloud Data Store.
- The Add AWS/Azure/Google Cloud Data Store screen appears with a name of the specified recovery point server.
- Navigate to Destinations > Data Stores.
- On the Data Store page, click Add Data Store, and then select Add AWS/Azure/Google Cloud Data Store.
- The Add AWS/Azure/Google Cloud Data Store screen appears.
- Specify the following details:
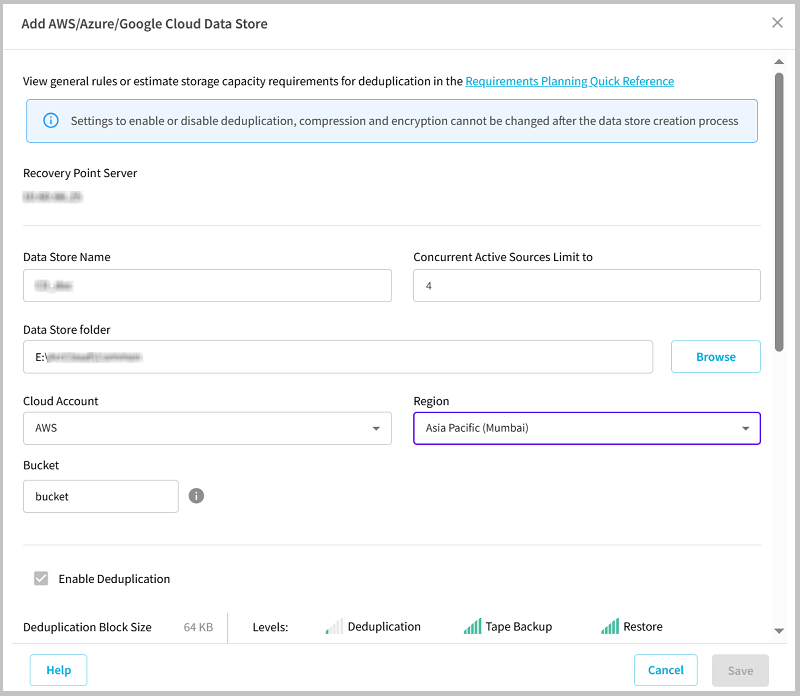
- Data Store Name: Specifies the name of the data store.
- Concurrent Active Sources Limit to: Specifies the maximum concurrent active sources on the data store.
- Default Value: 4
- Data Store folder: Refers to the location of the folder where the data store is created. Type the local full path or click Browse to navigate and select the desired local folder.
- Cloud Account: Select the cloud account from the drop-down list as needed.
- Note: If you have added a single cloud account to the Console, it is selected by default.
- Region: Select the region for the cloud account as needed.
- Bucket: Refers to the bucket name that you want to use as a Cloud destination. All files and folders moved or copied to the cloud vendor are stored and organized in your buckets (or containers). Buckets are fundamental containers used to group and organize your files. Every object stored with the cloud vendor is placed in a bucket. For more information about naming convention, see Bucket Name Convention.
-
- Data Store Name: Specifies the name of the data store.
- Concurrent Active Sources Limit to: Specifies the maximum concurrent active sources on the data store.
- Default Value: 4
- Data Store folder: Refers to the location of the folder where the data store is created. Type the local full path or click Browse to navigate and select the desired local folder.
- Cloud Account: Select the cloud account from the drop-down list as needed.
- Note: If you have added a single cloud account to the Console, the cloud account is selected by default.
- Region: Select the region for the cloud account as needed.
- Bucket: Refers to the bucket name that you want to use as a Cloud destination. All files and folders moved or copied to the cloud vendor are stored and organized in your buckets (or containers). Buckets are fundamental containers used to group and organize your files. Every object stored with the cloud vendor is placed in a bucket. For more information about naming convention, see Bucket Name Convention.
- JSON Key File: Browse to the location where the JSON key file is saved. Select the JSON file, and then click OK. For more information, see Create a Service Account and Private Key.
- Note: The JSON Key File field appears only when you select the cloud region for the Google Cloud Platform cloud service.
- Endpoint: Refers to the vendor service URL. This field gets auto-filled and grayed out for the Google Cloud Platform cloud service.
- Note: The Endpoint field appears only when you select the Other option as the cloud region for the Google Cloud Platform cloud services.
-
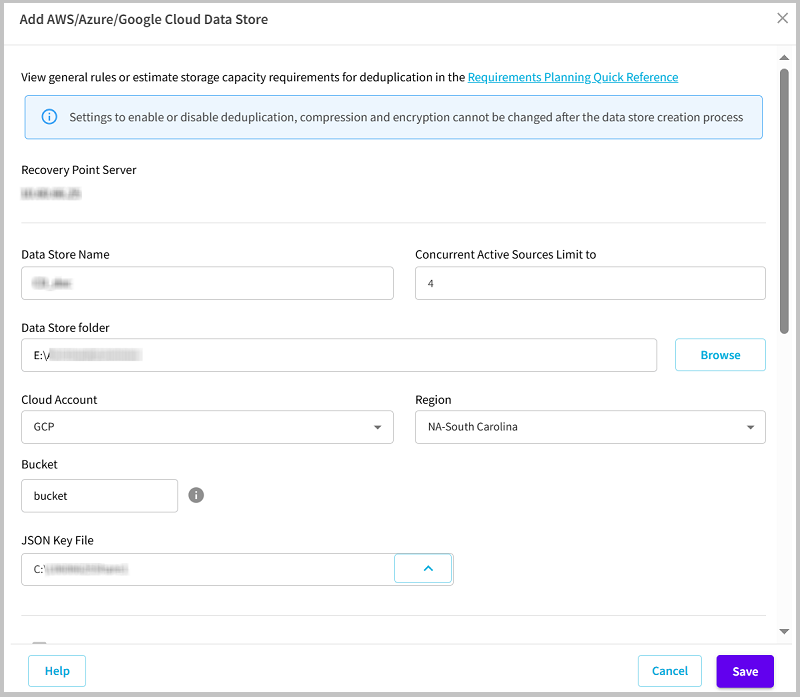
- Data Store Name: Specifies the name of the data store.
- Concurrent Active Sources Limit to: Specifies the maximum concurrent active sources on the data store.
- Default Value: 4
- Data Store folder: Refers to the location of the folder where the data store is created. Type the local full path or click Browse to navigate and select the desired local folder.
- Cloud Account: Select the cloud account from the drop-down list as needed.
- Note: If you have added a single cloud account to the Console, the cloud account is selected by default.
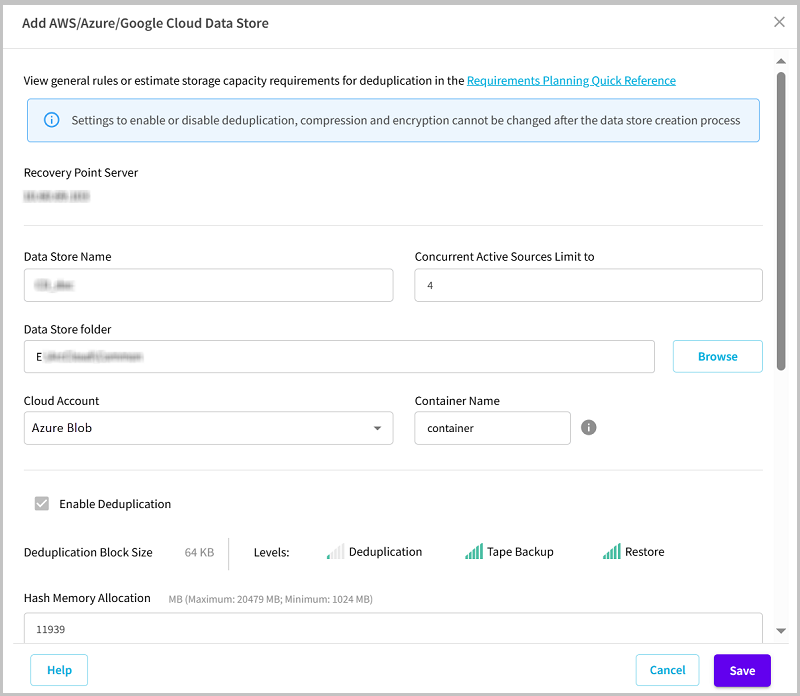
- Container Name: Refers to the name of a container that you want to use as a Cloud destination. A storage account contains an unlimited number of containers, and a container can store an unlimited number of blobs and organizes a set of blobs in a file system. While creating a container name, make sure to meet the naming conventions. For more information, see Naming and Referencing Containers, Blobs, and Metadata.
- Note: The Container Name field appears only for the Microsoft Azure Blob cloud account.
-
- Provide the following details, and then click Save:
- Enable Deduplication: Specifies that deduplication is enabled for this data store. Cloud Console supports both types of deduplication: Source-side deduplication and Global deduplication. Source-side deduplication prevents duplicate data blocks to move across network from a particular agent. Global deduplication eliminates duplicate data across all client machines based on the volume cluster level. By default, the Enable Deduplication check box is selected and grayed out.
- Deduplication Block Size: By default, the deduplication block size is selected as 64 KB.
- Hash Memory Allocation: Type the amount of physical memory that you want to allocate to keep hashes. This field is pre-filled with a default value. The default value is based on the following calculation:
- If the physical memory of the RPS is smaller than 4 GB (or is identical to 4 GB), the default value of Hash Memory Allocation is identical to the physical memory of the RPS.
- If the physical memory of the RPS is greater than 4 GB, Cloud Console calculates the available free memory at this time. Assume that the available free memory is X GB at present. Cloud Console further checks the following conditions:
- If (X * 80%) > = 4 GB, the default value of Hash Memory Allocation is (X * 80%).
- If (X * 80%) < 4 GB, the default value of Hash Memory Allocation is 4 GB.
- Example: Consider the RPS has 32 GB of physical memory. Assume that operating system and other applications use 4 GB memory while creating the data store. So, the available free memory at this time is 28 GB. Then, the default value of Hash Memory Allocation is 22.4 GB (22.4 GB = 28 GB * 80%).
- Hash destination is on a Solid State Drive (SSD: Specifies that the hash folder is on a solid state drive.
- Note: Configure the hash destination on local SSD if the Hash destination is on a Solid State Drive(SSD) check box is selected.
- Index Destination: Defines the index destination folder to store the index files. Select a different disk to improve the deduplication processing.
- Note: The Index Destination path must be an empty folder.
- Hash Destination: Defines the path to store the hash database. Cloud Console uses the SHA1 algorithm to generate the hash for source data. The hash database manages the hash values. Selecting a high speed Solid State Drive (SSD) increases the deduplication capacity and requires a lower memory allocation. For better hash performance, we recommend you that format the SSD volume as NTFS file system with 4 KB volume cluster size.
- Note: The Hash Destination path must be an empty folder.
- Notes:
- You cannot specify the same path for the following folders: Data Store folder, Index Destination, and Hash Destination.
- Remote or network share paths are not supported for Cloud data stores.
- Enable Compression: Specifies that the data compression settings are enabled.
- Compression Type: Specifies whether to use the Standard or Maximum as the compression type.
- Compression is often selected to decrease the usage of the disk space, but also has an inverse impact on your backup speed due to the increased CPU usage. Based on your requirement, you can select one of the three available options.
- Enable Encryption: Specifies that encryption settings are enabled. When you select this option, you must specify and confirm the encryption password.
- Data encryption is the translation of data into a form that is unintelligible without a deciphering mechanism. The Arcserve UDP solution uses secure, AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) encryption algorithms to achieve maximum security and privacy of your data. For data stores, encryption or No encryption is supported. For Encryption, only AES-256 is available.
- A password is not required when you are attempting to restore to the computer from which the backup was performed. However, when you attempt to restore to a different computer, a password is required which is set in the policy and not the password set in the data store.
- Note: After the data store is created, you cannot enable or disable deduplication, compression, or encryption.
- The specified AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud data store is added successfully.